The Nine P’s/9P’s of Marketing ©2007* are Planning, Product, Price, Place, Promotion, Partners, People, Passion and Presentation created by Larry Steven Londre. They are used in the marketplace, Marketing Seminars, Advertising Classes, the Classroom and the Courtroom. This Marketing concept includes important strategic philosophies and practices which guide Marketing planning, objectives, strategies, tactics, efforts and/or Marketing relationships/partnerships/alliances.
Product companies, service firms, “for profits” entities and nonprofits “selling” directly or indirectly to consumers (B2C), to marketing intermediaries (such as industrial, consumer, retail, wholesale and professional channels of distribution), and to other businesses (B2B) are using the nine P’s of Marketing.
Developing a strong brand is a byproduct. It comes from doing the components under the Nine P’s of Marketing…right. Make sure the Product or Service is excellent. Research and Planning, excellent.
These are some of the reasons Larry Steven Londre, as an experienced marketing professional, marketing expert, adman, marketing consultant and teacher of Marketing, Advertising and Business Strategies; created the Nine P’s of Marketing .
Using the 9P’s of Marketing help brand managers, marketing managers, entrepreneurs and others work within a structure with tools of observation plus research and for new product development, customer service, market implementation, securing better partners, strategic promotion, better presentation of products, firms and organizations.
Download 2025e Version of 9Ps PDF | Download 9Ps PDF (Condensed) | The first “P” >*Created by Larry Steven Londre. Copyright 2007.


Good Marketing decision making is no accident. It takes insight and insights.
Employees, managers, staff, people and organizations engage in a number of tactics and activates we call Marketing. But it’s much more. It starts with planning. I have found over the years that many seem to confuse advertising with Marketing or Marketing with advertising. There is so much more to marketing than one component under Promotion.
Using the Nine P’s of Marketing help brand managers, marketing managers, entrepreneurs and others work within a structure with tools of observation plus research and for new product development, customer service, market implementation, securing better partners, strategic promotion, better presentation in the marketplace and much more.
Develop and transform marketing objectives to marketing strategies to tactics, marketing management must make basic decisions on marketing targets, marketing mix, pricing, promotion, partnerships, distribution, marketing budgets/expenditures and marketing allocations.
It’s dividing the total marketing budget among the various tools in the marketing mix and for the various products, channels and distribution, promotion, partners, presentation media, sales areas and others.
The 9P’s start with Planning and Research.
Click here for more examples and detail.


Product mix, features, branding, designs, packaging, sizes, services, maintenance contracts, warranties, return policies.
A Product (service) is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need. (Kotler)
Look at branding; brand equity; brand name; quality; unique selling proposition (USP) and unique value proposition (USP); newness; complexity; physical appearance; packaging; labeling; ingredients; maintenance and service contracts; and others.
A product line is a group of products that are closely related because they function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer groups, are marketed or sold through the same types of outlets, or fall within given price ranges. The major product line decision involves product line length (the number of items in the product line. A company’s product mix has four important dimensions: width (number of different product lines), length (number of items a company carries within the product lines), depth (number of versions offered for each product in the line), and consistency (how closely related the various product lines are in end use, production requirements, distribution channels, or in any other way).
Click here for more examples and detail.


Set of buyers who share common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve. Targeting.
A Target Market consists of a set of buyers who share common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve. Market targeting can be carried out at several different levels.
A product focusing on a specific target market contrasts sharply with one following the marketing strategy of mass marketing. A target audience would be a media term.
Defining a target market requires market segmentation; the process of segmenting the entire market as a whole and separating it into manageable units based on demographics, geographics, psychographics, behavior, technographics or technographical characteristics.
Can the segments be accessed?


Pricing includes wholesale/retail/promotional prices, discounts, trade-in allowances, quantity discounts, credit terms, sales and payment periods and credit terms. Pricing decision making also involves adjusting prices concerning the competitive environment, economic situations and involve buyer perceptions.
“Pricing” is the sum of the values that customers exchange for the benefits of having or using the product or service.
Deceptive and misleading pricing practices may lead potential buyers and consumers to believe they will get more value and a better price than they will actually receive.
Consider and review “Value-pricing” and “Perceived-pricing.” “Value,” the worth in monetary terms of the technical, economic service and social benefits a customer receives in exchange for the price he or she pays for a market offering. Look at good, better, best pricing and values.
The “value” that the customer perceives in relation to the price paid must be greater than alternatives in order for a selected product to be purchased.
Prices are a key positioning factor and must be decided in relation to the target market, the product and service assortment mix, and the competition. All retailers would like high turns x earns (high volumes and high gross margins), but the two don’t usually go together. Most retailers fall into the high-markup, lower volume group (fine specialty stores) or the low-markup, higher-volume group (mass merchandisers and discount stores). (Kotler and Keller)
Pricing strategies include: cost-, profit-, competition-, demand-, value-, customer led-based pricing.
Click here for more examples and detail.


The communication element includes personal and non-personal communication activities. Activities that communicate the merits of the overall product, which include looking at consistency of message and messaging, especially with and within the different targets/elements/components/parts.
Eight (8) major, strategic components of Promotion:









Look at “real” product and service experiences. Look at purpose, presentation and branding affecting messaging and buying behaviors.
The “P” is the act and purpose of strategically presenting any of the different 9P’s© to your customers, suppliers, wholesalers, retailers, sales force, marketing intermediaries, clients, employees, and/or partners. They are symbols or images that represent something; a descriptive or persuasive account (as a sales person of the product or service). Something set forth for the attention of mind.
Think about positive and negative emotions in a presentation by a salesperson or sales force. Negative emotions narrow a person’s vision and propel selling behavior toward survival in the moment, especially new sales people– “I’m frightened, so I’ll flee.” Positive emotions do the opposite: They broaden people’s ideas and we sell longer and can be more perceptive, more creative. For the seller, positive emotions can widen our view of the potential buyer and the specific situation. Where negative emotions help us see trees, positive ones reveal forests. They can aid in devising unexpected solutions to the buyer’s problem. The effects of positivity during a sales experience can infect the buyer, making him or her less adversarial, more open to the possibility and more willing to make a purchase.
Wal-Mart and retailers want a better integration of its retailing in store and online.
Another example or two: The Internet changed everything especially in the “presentation” of the different P’s. Another part of “presenting” is the big picture perspective of corporate social responsibility (CSR) which refers to consideration of, and the firm’s responses to issues, beyond narrow economic, technical and legal requirements. These objectives and firm strategies of accomplishing social benefits along with the traditional economic gains which the firm is seeking is vitally important to the “presentation” to the constituents, different publics and to the world.
Companies look and review issues of global sustainability, not interfering in the internal politics of the different countries and the governments of local markets, respecting natural resources, conducting research and development activities in developing countries, respecting local laws and regulations, environmental concerns, creating jobs in the served markets, respecting human rights, and more.
Click here for more examples and detail.

A strong liking for or devotion to some activity; deep interest in your partnership/presentation of any of the 9P’s© to any target or partner.
As a brand manager or marketing manager it starts with “believing” in the product and services you market and sell. And from research, it needs to show, in the “presentation,” your passion for the product. Many sales persons dispute the concept that many sales people can sell anything, whether they believe in the product or not.
That may have been true in the past, before the web, when manufacturers, producers and sellers held distinct information and specific product advantages, with buyers having limited choices. Not now. Today, buyers can find tons of information about products, product lines, product variables, product attributes, distribution options, strategic partnerships, pricing, sales promotions, new product development, and more.
Salespeople have told me that believing leads to a deeper understanding of your product offerings, which allows sellers to better match what they have with what others need and buyers want. According to psychologists, with “passion,” management, brand managers, marketing managers and other employees need another component or two. Needing to extend commitment over a period of time, add inspiration, longevity with perseverance to heighten passion. When you combine inspiration, passion with perseverance, the team may have “grit,” in delivering short and long term sales.
Click here for more examples and detail.
Start with planning, process and an analysis of the Nine P’s (9P’s). Planning includes observing what to do and what not to do in the marketplace. It includes research and developing a vision for each of the remaining Nine P’s.
In his influential 1965 textbook Business Policy: Text and Cases by Kenneth R. Andrews, he did not set out to detail the concept of “what strategy is,” under “Planning.” Instead he said that he chose to “sidestep the problem of drawing distinctions between objectives, policy and programs of action. I would put them in several categories but specifically under “Planning” and “Execution,” in the Nine P’s.
According to Andrews, strategy or strategies are the pattern or patterns of decisions in a company or firm that determine and reveal its objectives, purposes or goals, produces the principle policies and plans for achieving those goals, plus defines the range of businesses the company is to pursue, the kind of economic and human organization it intends to be, and the nature of the economic and non-economic contributions it intends to make to its shareholders, employees, customers, and communities.

Some products from Apple are “perceived” to have a better user experience, a better design, a better presentation, which are also shared by both users and non-users. But Fast Company reported that it’s the engineering culture of the company and the way the whole organization is structured that help support product design. Everyone in the organization is striving and thinking about better designed products for the marketplace…making a better presentation of products and services to users and potential users.
A product (service) is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need. Example is from this Havana bar in Cuba. Their differentiation is any patron and others can sign their name or add their initials to the walls, tables or window frames. Anything.
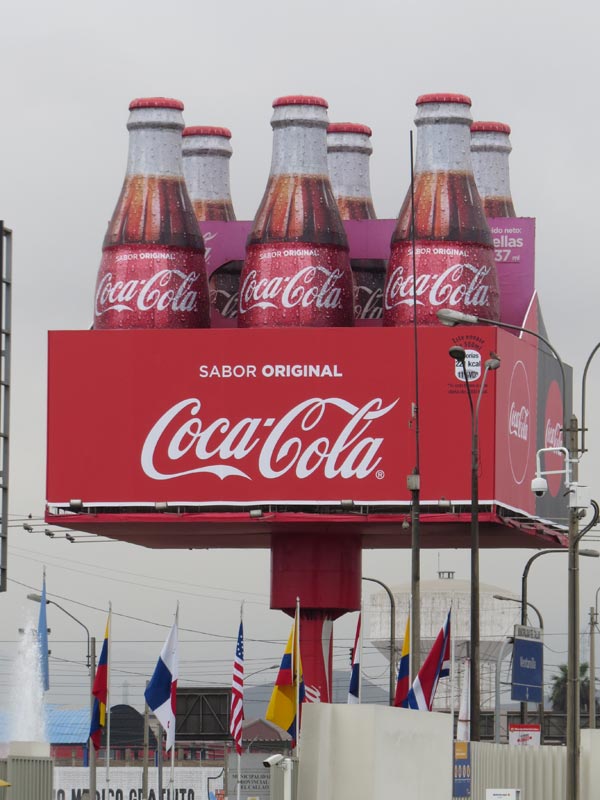
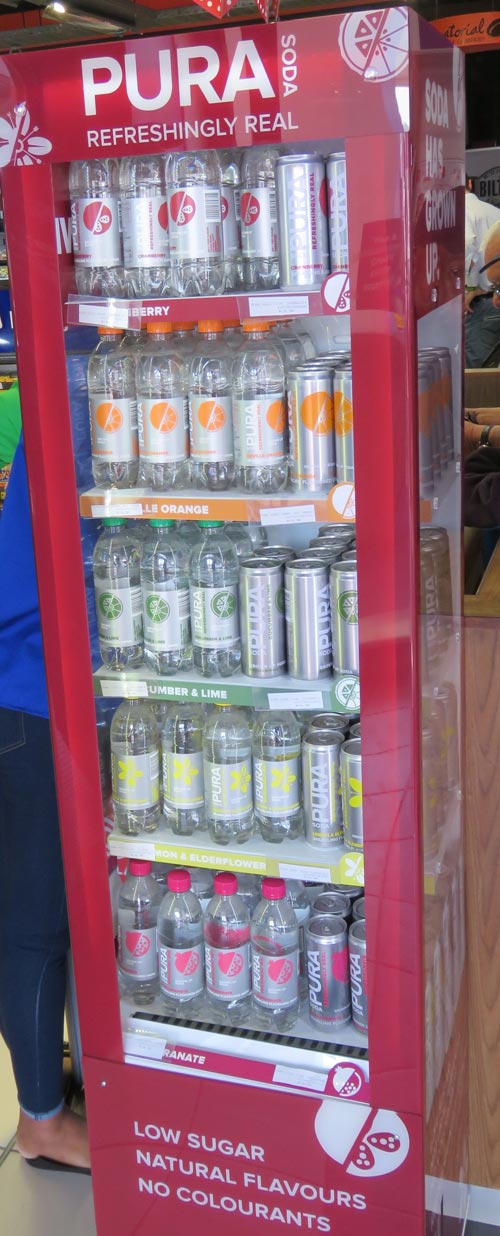
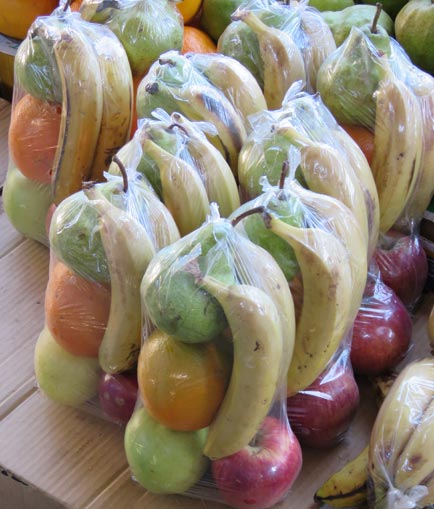
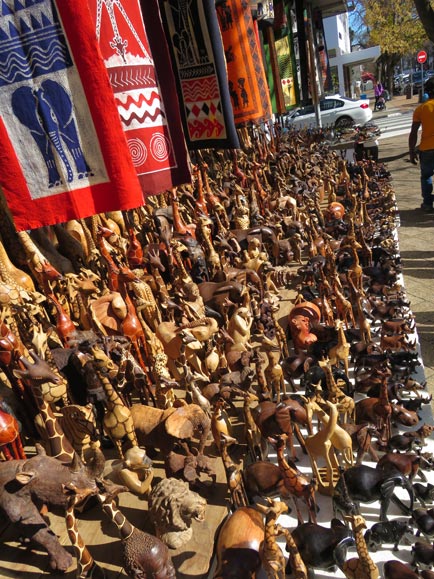

















Companies, advertising agencies and advertisers are trying lots of ways to target people who don’t really see the ads (they may be too small on a smartphone), they are multi-tasking, fast-forwarding through TV spots, ignore print ads or there’s too much clutter.
Can the segments be accessed?
Marketing strategies need to be adapted for the different tiers or segments. Instead of viewing the market as a uniform group of customers with similar potential, the firm needs to view them as distinct groups or segments with differing potential.




The “value” that the customer perceives in relation to the price paid must be greater than alternatives in order for a selected product to be purchased. (Anderson and Narus, Business Market Management, Understanding, Creating, and Delivering Value, 1999)
Prices are a key positioning factor and must be decided in relation to the target market, the product and service assortment mix, and the competition. All retailers would like high turns x earns (high volumes and high gross margins), but the two don’t usually go together. Most retailers fall into the high-markup, lower volume group (fine specialty stores) or the low-markup, higher-volume group (mass merchandisers and discount stores). (Kotler and Keller)







Should we promote? What should we promote? To whom should we promote? What economic and discount levels should we offer? What form of promotion should we offer? What features? How frequent?
Mobile marketing and advertising, as cell phones/mobile devices keep changing and turn into multi use devices including payment activators. The mobile device and/or cell phone is a very personal medium. Can be on 24/7, people and potential shoppers run their lives off of mobile. It’s business, it’s personal, and it’s information generating/gathering/forwarding. It’s been referred to as “a brand in the hand” or “brands in the hands.”
Samsung has used pop-up stores and customers can leave with a device, smartphones, tablets and wrist devices, free of charge. An “event and experience” initiative to convince smartphone and tablet owners to switch to Samsung. They also cover the wireless data costs.








Example: In 2015, Subway is selling 80% of its new franchise locations to existing franchisees. More than half of the locations are non-traditional including schools, zoos, military bases, plus hospitals. Where there are “captive audiences,” or under “People.” (Bloomberg.com and subway.com)






In the 2014 Academy Awards, Ellen DeGeneres with Bradley Cooper, Meryl Streep, Jennifer Lawrence and others took a “selfie” with a Samsung’s Galaxy Note 3. The product placement was negotiated as part of a $20 million broadcast buy, for this major sponsor of the telecast.
It’s estimated that USPS handled 40% of Amazon’s volume in 2014, almost 150 million items. Let’s add some “Price” to this: It’s estimated that each package is $2 heavily discounted or about 50% of what UPS or FedEx charges. (Bloomberg.com , August, 2015)

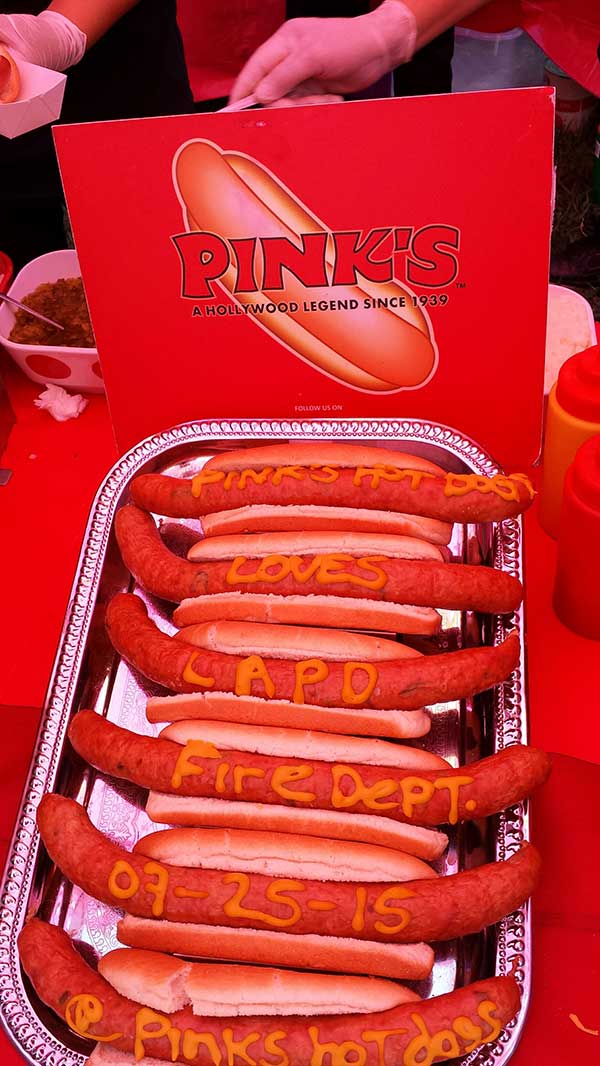

An employee example: Companies can define and refine their “employment” brand or branding. An organization’s “employment brand” should represent a promise to candidates and potential employees that reflects the organization’s mission. Why do you want to work here…or why we want you to work here. From ERE.net, finding and “winning over,” better candidates may include boldness and unusualness, plus an emphasis on their candidate’s aspirations rather than pay of compensation.
Selling and purchasing wine with in store music playing: In 1999, psychologists from the University of Leicester found that the type of music playing in a store could influence which wines were purchased: when French music was playing, people bought French wines; when German music was turned on, German wines outsold the rest. The customers remained oblivious, and unaware of the business test.



Apple is one of the masters at creating huge excitement around an idea; new product category or product intervention and introduction.
“Las Vegas Means Business:” Many “People” and marketing decision makers in Las Vegas found that the old slogan “What Happened in Vegas, Stays in Vegas” had a negative effect on tourism, meetings and conventions. Las Vegas is quoting research or Planning that “88% of executives agree that having events (sales presentations/trade shows) in Las Vegas makes their job easier.”


For 40+ years, he has taught and presented the Nine/9P’s/4P’s of Marketing at many
colleges and universities including undergraduate and graduate programs at:


Companies do not get potential users or customers to try a product by convincing them to love their brand. You get them to love a brand by convincing them to try and use the product or service.
Be sure the company is taking good care of their customers (People), and having the right Planning and targeting (People), the right Product, right Place or distribution, right Price, right Promotion, right Partners, right Presentation, with the right amount of Passion.
“The aim of Marketing is to know and understand the customer so well that the product or service fits them and sells itself.”
Copyright 2014, 2026 Londre Marketing Consultants, LLC
